The certificate signing request![]() A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. (CSR
A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. (CSR![]() A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA.) enrollment
A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA.) enrollment![]() Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). page provides the ability to submit a CSR and download the resulting certificate.
Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). page provides the ability to submit a CSR and download the resulting certificate.
To request a certificate via CSR:
- Generate a CSR. This can be done within the target application (e.g. Microsoft IIS), by using a tool such as certutil or OpenSSL, or by using the Keyfactor Command CSR generation tool (see CSR Generation).
- In the Management Portal, browse to Enrollment > CSR Enrollment.
-
Paste your CSR into the CSR Content text area, with or without the BEGIN REQUEST/END REQUEST delimiters.
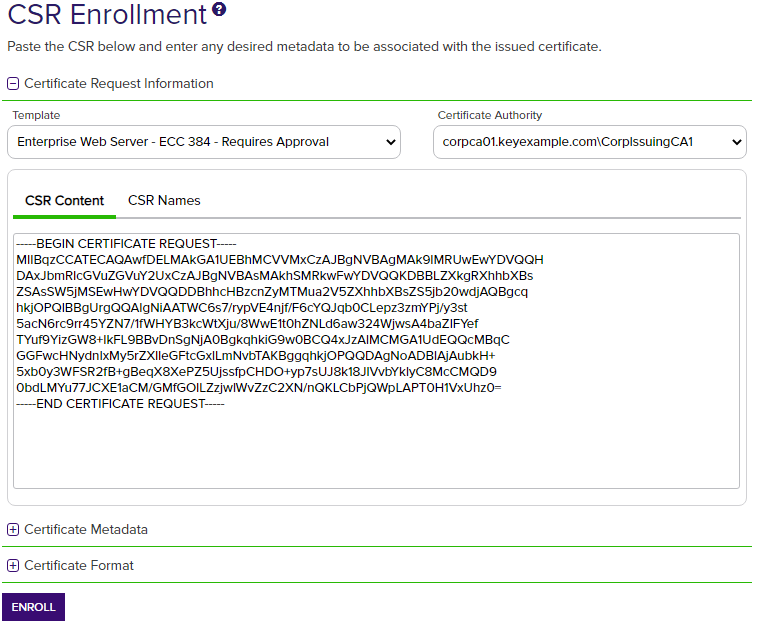
Figure 92: CSR Enrollment: CSR Content
-
The CSR contents will be parsed, and you will automatically be switched to the CSR Names view. Review the data to be sure it is as expected.
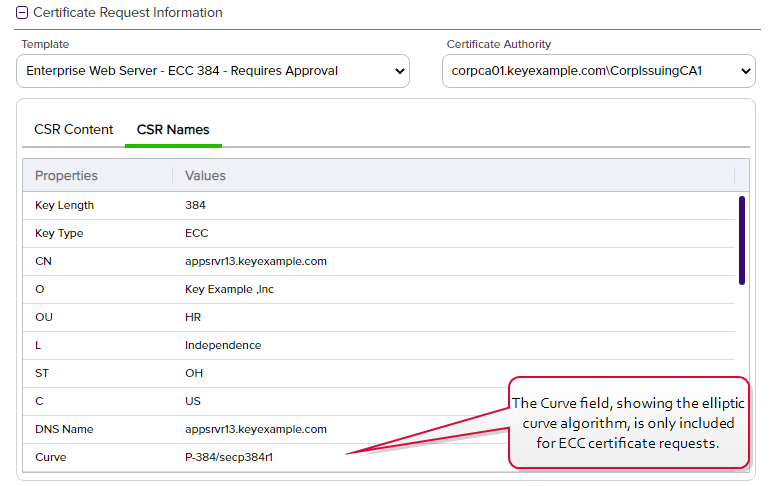
Figure 93: CSR Enrollment: CSR Names
Note: If a system-wide or template-level regular expression exists for a subject part or SAN The subject alternative name (SAN) is an extension to the X.509 specification that allows you to specify additional values when enrolling for a digital certificate. A variety of SAN formats are supported, with DNS name being the most common., and the subject part or SAN is left blank, the regular expression will be applied to an empty string for that part. For example, if you have a regular expression on organization, but do not supply an organization, the regular expression will be applied to a blank string as if that were supplied as the organization.
The subject alternative name (SAN) is an extension to the X.509 specification that allows you to specify additional values when enrolling for a digital certificate. A variety of SAN formats are supported, with DNS name being the most common., and the subject part or SAN is left blank, the regular expression will be applied to an empty string for that part. For example, if you have a regular expression on organization, but do not supply an organization, the regular expression will be applied to a blank string as if that were supplied as the organization. -
If you are enrolling from an enterprise CA
 A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA., select a certificate template from the Template dropdown. The templates are organized by configuration tenant
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA., select a certificate template from the Template dropdown. The templates are organized by configuration tenant A grouping of CAs. The Microsoft concept of forests is not used in EJBCA so to accommodate the new EJBCA functionality, and to avoid confusion, the term forest needed to be renamed. The new name is configuration tenant. For EJBCA, there would be one configuration tenant per EJBCA server install. For Microsoft, there would be one per forest. Note that configuration tenants cannot be mixed, so Microsoft and EJBCA cannot exist on the same configuration tenant. (formerly known as forest
A grouping of CAs. The Microsoft concept of forests is not used in EJBCA so to accommodate the new EJBCA functionality, and to avoid confusion, the term forest needed to be renamed. The new name is configuration tenant. For EJBCA, there would be one configuration tenant per EJBCA server install. For Microsoft, there would be one per forest. Note that configuration tenants cannot be mixed, so Microsoft and EJBCA cannot exist on the same configuration tenant. (formerly known as forest An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers.). If you have multiple configuration tenants and templates with similar names, be sure to select the template in the correct configuration tenant.
An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers.). If you have multiple configuration tenants and templates with similar names, be sure to select the template in the correct configuration tenant.
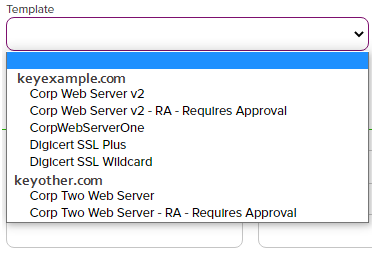
Figure 94: Select a Certificate Template
-
Select the Certificate Authority from which the certificate should be requested. Only CAs that have the selected template available for enrollment or are standalone, if you check the stand-alone CA box, will be shown.
Tip: If you are enrolling from a standalone CA, check the Use a stand-alone CA box instead of selecting a template. The check box for stand-alone CAs only appears if you have a stand-alone CA configured for enrollment.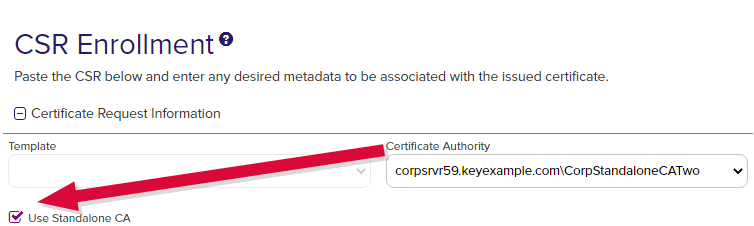
Figure 95: CSR Enrollment for Stand-Alone CA
-
The SAN section of the page appears if you enable the Allow CSR SAN Entry application setting (see Application Settings: Enrollment Tab). This option is disabled by default. In the Subject Alternative Names section of the page, click Add and select from the dropdown to enter one or more SANs for your CSR. Use the Remove action button to remove an existing SAN. The SAN field supports:
-
DNS
 The Domain Name System is a service that translates names into IP addresses. name
The Domain Name System is a service that translates names into IP addresses. name -
IP version 4 address
-
IP version 6 address
-
User Prinicpal Name
-
Email
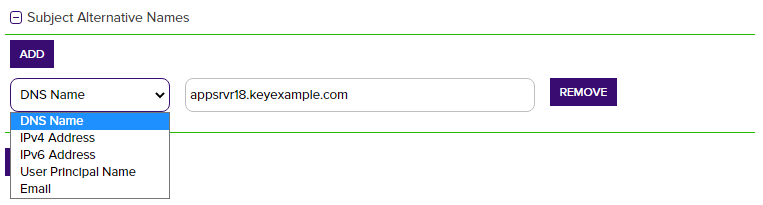
Figure 96: CSR Enrollment SAN options
Important: If the RFC 2818 compliance setting is enabled for the selected template (see Certificate Template Operations), your request must have at least one SAN either included in the original CSR or entered separately in this field, which matches the CN A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). in the request.Note: Entering SANs here may either append or overwrite the SANs in the CSR request depending on how the issuing CA is configured. Please be sure to check that the certificate has the correct SANs after issuance. Any SAN added automatically as a result of RFC 2818 compliance settings at the policy handler level will still be added alongside anything you add here. For more information, review the SAN Attribute Policy Handler for the Keyfactor CA Policy Module (see Installing the Keyfactor CA Policy Module Handlers in the Keyfactor Command Server Installation Guide).
A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). in the request.Note: Entering SANs here may either append or overwrite the SANs in the CSR request depending on how the issuing CA is configured. Please be sure to check that the certificate has the correct SANs after issuance. Any SAN added automatically as a result of RFC 2818 compliance settings at the policy handler level will still be added alongside anything you add here. For more information, review the SAN Attribute Policy Handler for the Keyfactor CA Policy Module (see Installing the Keyfactor CA Policy Module Handlers in the Keyfactor Command Server Installation Guide). -
-
If template-specific enrollment fields have been defined (see Enrollment Fields Tab) for the selected template, the fields will display in the Additional Enrollment Fields section. The types of fields shown could be either blank (string) fields or multiple choice drop-down fields depending on how they were configured on the template. All additional enrollment fields are mandatory.

Figure 97: Populate Enrollment Fields
-
In the Certificate Metadata
 Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. section of the page, populate any defined certificate metadata fields (see Certificate Metadata and Metadata Tab) as appropriate for the template. These fields may be required or optional depending on your metadata configuration. Required fields will be marked with *Required next to the field label. Any completed values will be associated with the certificate once it has been synchronized with Keyfactor Command.
The order in which the metadata fields appear can be changed (see Sorting Metadata Fields).
Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. section of the page, populate any defined certificate metadata fields (see Certificate Metadata and Metadata Tab) as appropriate for the template. These fields may be required or optional depending on your metadata configuration. Required fields will be marked with *Required next to the field label. Any completed values will be associated with the certificate once it has been synchronized with Keyfactor Command.
The order in which the metadata fields appear can be changed (see Sorting Metadata Fields).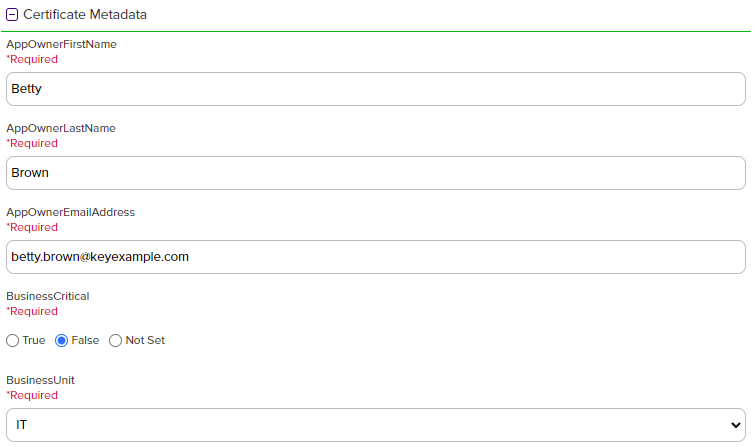
Figure 98: Populate Metadata Fields
-
At the bottom of the page, select the radio button for the desired encoding format (PEM
 A PEM format certificate file is a base64-encoded certificate. Since it's presented in ASCII, you can open it in any text editor. PEM certificates always begin and end with entries like ---- BEGIN CERTIFICATE---- and ----END CERTIFICATE----. PEM certificates can contain a single certificate or a full certifiate chain and may contain a private key. Usually, extensions of .cer and .crt are certificate files with no private key, .key is a separate private key file, and .pem is both a certificate and private key. or DER
A PEM format certificate file is a base64-encoded certificate. Since it's presented in ASCII, you can open it in any text editor. PEM certificates always begin and end with entries like ---- BEGIN CERTIFICATE---- and ----END CERTIFICATE----. PEM certificates can contain a single certificate or a full certifiate chain and may contain a private key. Usually, extensions of .cer and .crt are certificate files with no private key, .key is a separate private key file, and .pem is both a certificate and private key. or DER A DER format certificate file is a DER-encoded binary certificate. It contains a single certificate and does not support storage of private keys. It sometimes has an extension of .der but is often seen with .cer or .crt.).
A DER format certificate file is a DER-encoded binary certificate. It contains a single certificate and does not support storage of private keys. It sometimes has an extension of .der but is often seen with .cer or .crt.).
Figure 99: Select a Certificate Format
-
Click the Enroll button to begin the certificate request process.
- If the request completes successfully, you'll see a success message and you'll be prompted by your browser to begin download of your certificate.
-
If the template you selected requires approval at the Keyfactor Command workflow level, you'll see a message that your request is suspended and is awaiting one or more approvals. The user(s) responsible for approving the request will be notified (if the workflow has been configured this way, see Adding, Copying or Modifying a Workflow Definition). You can use the My Workflows Created by Me tab (see Workflows Created by Me Operations) to check on the status of your request. If the Management Portal feature has been configured to send notification alerts when a certificate is issued following approval, you may receive an email message when your certificate is available for download. The email message may contain a download link. See Issued Certificate Request Alerts.
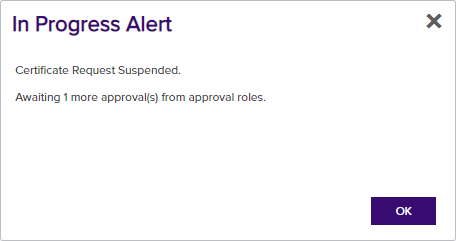
Figure 100: CSR Enrollment Completed Successfully—Awaiting Workflow Approval(s)
-
If the template you selected requires manager approval at the CA level, you’ll see a message that your request is pending. The user responsible for approving issuance of pending certificates will be notified (if that Management Portal feature is configured, see Pending Certificate Request Alerts). You can use the Certificate Requests page (see Certificate Requests) to check on the status of your pending request and complete the certificate download. If the Management Portal feature has been configured to send notification alerts when a pending certificate request is approved or denied, you may receive an email message when your certificate is available for download. The email message may contain a download link. See Issued Certificate Request Alerts and Denied Certificate Request Alerts.
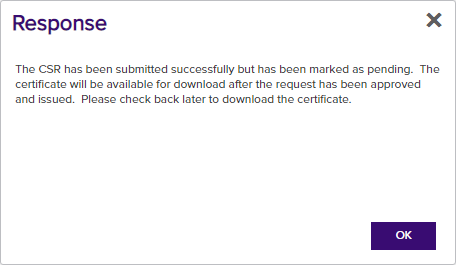
Figure 101: CSR Enrollment Completed Successfully—Pending Status
You can also find the help icon at the top of the page next to the Log Out button. From here you can choose to open either the Keyfactor Command Documentation Suite at the home page or the Keyfactor API Endpoint Utility.